Increasing numbers of knee replacement surgeons who want longer-lasting implants and faster recoveries for their patients are turning to cementless options. Once held back by inconsistent fixation and limited surgeon familiarity, cementless implant technology is now gaining momentum thanks to evolving and innovative designs and growing clinical validation.
According to the AAOS American Joint Replacement Registry, the use of cementless fixation was used in 22% of all primary total knee arthroplasties (TKAs) performed in 2023, up from 2% in 2012. That upward trajectory is expected to continue.
“Clinicians are looking to increase implant longevity in younger, more active patients,” said Jordan Wagner, Vice President of Marketing at restor3d. “The growing TKA volumes in younger patients has increased the interest in durable fixation that can better accommodate higher activity levels and potentially reduce revision rates later in life — something cementless designs are well-positioned to address.”
Proven Performance
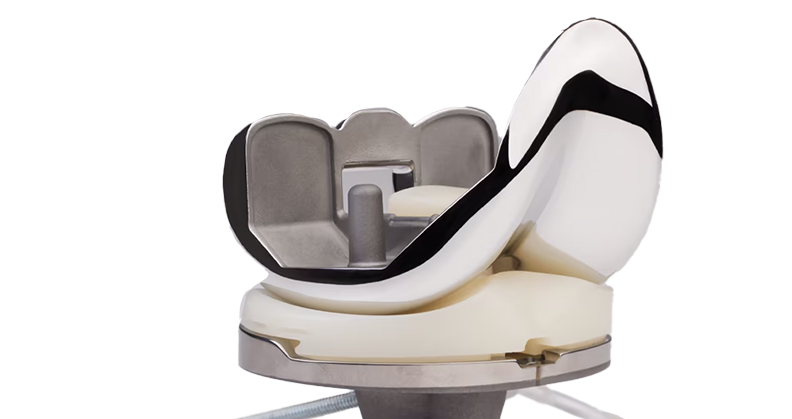
Cementless knee implants have been used successfully in knee replacement for decades, but recent advances in technologies like 3D printing have increased their clinical efficacy.
“The industry has seen a significant increase in cementless knee replacement as surgeons look to more advanced technological offerings that can meet the needs of their younger patients,” said Peter Cipolletti, Senior Director of Marketing, Knee & Advanced Surgical Technology at Exactech.
Joe Urban, Global Knee President at Zimmer Biomet, pointed to implant design, case costs and operating room efficiencies as key drivers of adoption. He noted that operative time is up to 11 minutes shorter with cementless TKA compared to when cemented implants are used.
“There are a number of factors contributing to the interest in cementless TKA,” Urban said. “Biological surfaces and implant designs aimed at better fixation have led to improved outcomes, and cementless fixation has demonstrated gains in reduced operative times and lower overall costs due to the elimination of cementing accessories.”
Recent data show cementless implants performing on par — or better — than cemented options. For instance, Urban noted that Zimmer Biomet’s Oxford Cementless Partial Knee has demonstrated a 94% survivorship at 10 years.
Avoiding cement may also help reduce the risks of certain adverse surgical outcomes.
“Patients benefit because cementless implants avoid complications that are related to the use of cement, such as third-body wear and osteolysis,” Wagner said. “Possible thermal necrosis from cement polymerization is also prevented.”
Additionally, cementless designs offer potential advantages for bone preservation. “Since cementless implants directly contact the bone and rely on osseointegration for fixation, there is no need to remove additional bone around the implants to allow for an adequate cement mantle,” Wagner said.
However, Cipolletti cautioned that bone preservation isn’t guaranteed by the fixation method alone.
“Cementless implants don’t specifically enhance bone preservation,” he noted. “That said, cementless systems feature a cylindrical box resection that removes 30% less bone compared to traditional box resections.”
Surface Technology Advances
Success in cementless fixation hinges on surface engineering. All three companies we spoke to emphasized the critical role that surface coating and architecture play in supporting early and long-term fixation.
Zimmer Biomet’s Persona system incorporates OsseoTi Porous Metal Technology, which mimics the architecture of cancellous bone. “OsseoTi has demonstrated excellent integration with host bone as early as four weeks in an animal study,” Urban said.
He added that Zimmer Biomet also offers PPS (Porous Plasma Spray) Coating, which is designed to promote initial scratch-fit stability and long-term biologic fixation.
restor3d uses a fully additive manufacturing (AM) approach with its proprietary TIDAL Technology, a 3D-printed porous structure that’s engineered to closely replicate natural bone. “This promotes more consistent biologic fixation and bone in-growth,” Wagner said.
At Exactech, surface strategy has evolved beyond traditional coatings like hydroxyapatite, which were once used in combination with titanium plasma spray to encourage bone integration.
“By leveraging today’s advanced technologies like AM, implant design can be optimized to negate the necessity of additional chemical coatings while providing substantial increases to initial fixation and bone ingrowth,” Cipolletti said.
In the context of cementless knees, AM offers unparalleled flexibility in tailoring implant characteristics to meet diverse anatomical and mechanical requirements. Engineers can rapidly iterate design prototypes to refine pore size, shape and layout to enhance biological response and implant mechanics.
“AM has fundamentally changed the way we design cementless implants by allowing for precise control over pore geometry, porosity and surface architecture, something traditional manufacturing methods simply couldn’t achieve,” Wagner said.
Zimmer Biomet uses scanned images of knee structures in combination with 3D printing to build a structure that’s designed to replicate patient anatomy more closely, Urban noted.
“One of the main advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce monolithic components,” he said. “Historically, features of a component, like a tibia, would need to be produced in layers and bonded together.
With modern selective laser sintered 3D printing technology, the component can be produced from top to bottom as one continuous piece.”
Cipolletti noted that while the progress made in recent years with cementless technology is driven by AM, companies must still overcome obstacles to produce implants successfully and efficiently.
“Design or manufacturing challenges can arise while developing new technologies, but we find that they can be reduced by including the right surgeon and engineering experts early in the process,” Cipolletti said. “Striking the balance between strength and porosity was particularly challenging during the early development of our 3D printing technology, but our team iterated through testing to ultimately create a product that has proven initial fixation and long-term durability.”

The Truliant Porous Tibial Tray leverages additive manufacturing technology to create a porous structure that mimics the structure of cancellous bone.
Streamlined Solutions
Wagner pointed to multiple contributing factors for the continued growth of cementless knee replacements, including improved implant designs, a growing preference among surgeons and increasing numbers of outpatient procedures. She noted that hospitals and ASCs stand to benefit from cost savings and inventory reductions.
“Cementless implants can reduce operative time by eliminating cement mixing, pressurization and curing steps,” she said. “This offers potential workflow efficiencies and cost savings, particularly in high-volume outpatient arthroplasty programs.”
Cipolletti noted that the shift toward same-day surgery has played a critical role in the increased adoption of cementless knees.
“The outpatient environment depends on technologies like cementless knees, where maximizing surgical efficiency is of the utmost importance,” he explained. “As cases continue to move to same-day surgery settings, it’s expected that uncemented procedures will continue to experience the growth they have seen in recent years.”
Cementless knee systems have moved beyond niche status to become a central component of many orthopedic portfolios. As more players enter the space, differentiation through design, clinical performance and workflow optimization is essential.
To that end, some manufacturers are focusing on advanced instrumentation and streamlined delivery platforms. Zimmer Biomet, for example, offers integrated solutions that combine high-performing implants with tools that support intraoperative flexibility.
Urban noted that the company has engineered their solutions so that surgeons can pivot to cemented fixation mid-procedure, if necessary, without compromising outcomes.
“With the Persona OsseoTi Keel Tibia, the same cuts and similar prep allow surgeons to make an intraoperative decision on the best fixation for their patient, even if it means making a change to the preoperative plan,” he said.
Urban also emphasized that Zimmer Biomet’s cementless portfolio is designed to address broader clinical needs across patient populations.
“We have worked hard to develop implant solutions that leverage not only cementless technology but also other needs in the marketplace like partial knees, metal sensitivities and devices that address micromotion in older cementless designs,” Urban added. “With 3D printing capabilities, we can manufacture to meet the growing demand of our cementless solutions.”
restor3d is taking a fully personalized approach with its Identity 3DP Porous Total Knee system, reportedly the first of its kind. Each implant is designed from a patient’s CT scan to replicate their natural joint line and kinematics.
The company’s Knee in a Box solution also aims to simplify logistics in the O.R.
“The platform includes minimal reusable instrumentation, sterile-packed PSI and implants for seamless O.R. setup and turnover,” Wagner said. “This delivery model further enhances the time savings associated with removing the cementing step from knee replacement procedures.”
At Exactech, differentiation stems not only from implant design.
“The unique features between products exist in the way that we design our bone ingrowth surfaces, their interaction with supporting materials and the methodology in which we plan and execute the surgical procedure,” Cipolletti said.
Gaining Momentum
With compelling advantages in surgical efficiency, biologic fixation and long-term potential, cementless knees are well positioned for continued adoption. AM, personalized designs and patient demand for implant longevity are transforming the knee replacement landscape.
Increased surgeon familiarity is also accelerating the adoption of cementless knees.
“Recent registry data and peer-reviewed studies have shown comparable or superior outcomes with cementless knees, particularly in younger and healthier patients,” Wagner said. “As more surgeons gain experience and confidence with newer systems, adoption is steadily increasing.”
KK
Kendal Kloiber is a contributing editor.